Flat Feet In Adults (Adult Aquired FlatFoot)
Overview
The posterior tibial tendon serves as one of the major supporting structures of the foot, helping it to function while walking. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. PTTD is often called adult acquired flatfoot because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood. Although this condition typically occurs in only one foot, some people may develop it in both feet. PTTD is usually progressive, which means it will keep getting worse, especially if it isn't treated early.
Causes
The posterior tibial tendon, which connects the bones inside the foot to the calf, is responsible for supporting the foot during movement and holding up the arch. Gradual stretching and tearing of the posterior tibial tendon can cause failure of the ligaments in the arch. Without support, the bones in the feet fall out of normal position, rolling the foot inward. The foot's arch will collapse completely over time, resulting in adult acquired flatfoot. The ligaments and tendons holding up the arch can lose elasticity and strength as a result of aging. Obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase the risk of developing this condition. Adult acquired flatfoot is seen more often in women than in men and in those 40 or older.
Symptoms
Many patients with this condition have no pain or symptoms. When problems do arise, the good news is that acquired flatfoot treatment is often very effective. Initially, it will be important to rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and AAFD is usually made from a combination of symptoms, physical exam and x-ray imaging. The location of pain, shape of the foot, flexibility of the hindfoot joints and gait all may help your physician make the diagnosis and also assess how advanced the problem is.
Non surgical Treatment
Because of the progressive nature of PTTD, early treatment is advised. If treated early enough, your symptoms may resolve without the need for surgery and progression of your condition can be arrested. In contrast, untreated PTTD could leave you with an extremely flat foot, painful arthritis in the foot and ankle, and increasing limitations on walking, running, or other activities. In many cases of PTTD, treatment can begin with non-surgical approaches that may include. Orthotic devices or bracing. To give your arch the support it needs, your foot and ankle surgeon may provide you with an ankle brace or a custom orthotic device that fits into the shoe. Immobilization. Sometimes a short-leg cast or boot is worn to immobilize the foot and allow the tendon to heal, or you may need to completely avoid all weight-bearing for a while. Physical therapy. Ultrasound therapy and exercises may help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle following immobilization. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Shoe modifications. Your foot and ankle surgeon may advise changes to make with your shoes and may provide special inserts designed to improve arch support.
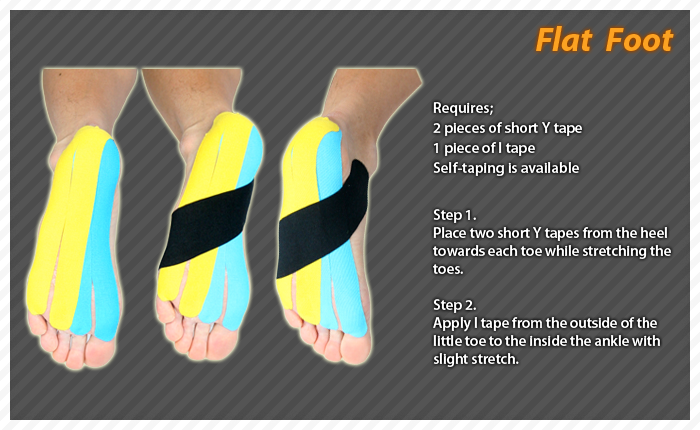
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually performed when non-surgical measures have failed. The goal of surgery is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve a patient?s mobility. More than one technique may be used, and surgery tends to include one or more of the following. The tendon is reconstructed or replaced using another tendon in the foot or ankle The name of the technique depends on the tendon used. Flexor digitorum longus (FDL) transfer. Flexor hallucis longus (FHL) transfer. Tibialis anterior transfer (Cobb procedure). Calcaneal osteotomy - the heel bone may be shifted to bring your heel back under your leg and the position fixed with a screw. Lengthening of the Achilles tendon if it is particularly tight. Repair one of the ligaments under your foot. If you smoke, your surgeon may refuse to operate unless you can refrain from smoking before and during the healing phase of your procedure. Research has proven that smoking delays bone healing significantly.
The posterior tibial tendon serves as one of the major supporting structures of the foot, helping it to function while walking. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. PTTD is often called adult acquired flatfoot because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood. Although this condition typically occurs in only one foot, some people may develop it in both feet. PTTD is usually progressive, which means it will keep getting worse, especially if it isn't treated early.

Causes
The posterior tibial tendon, which connects the bones inside the foot to the calf, is responsible for supporting the foot during movement and holding up the arch. Gradual stretching and tearing of the posterior tibial tendon can cause failure of the ligaments in the arch. Without support, the bones in the feet fall out of normal position, rolling the foot inward. The foot's arch will collapse completely over time, resulting in adult acquired flatfoot. The ligaments and tendons holding up the arch can lose elasticity and strength as a result of aging. Obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase the risk of developing this condition. Adult acquired flatfoot is seen more often in women than in men and in those 40 or older.
Symptoms
Many patients with this condition have no pain or symptoms. When problems do arise, the good news is that acquired flatfoot treatment is often very effective. Initially, it will be important to rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and AAFD is usually made from a combination of symptoms, physical exam and x-ray imaging. The location of pain, shape of the foot, flexibility of the hindfoot joints and gait all may help your physician make the diagnosis and also assess how advanced the problem is.
Non surgical Treatment
Because of the progressive nature of PTTD, early treatment is advised. If treated early enough, your symptoms may resolve without the need for surgery and progression of your condition can be arrested. In contrast, untreated PTTD could leave you with an extremely flat foot, painful arthritis in the foot and ankle, and increasing limitations on walking, running, or other activities. In many cases of PTTD, treatment can begin with non-surgical approaches that may include. Orthotic devices or bracing. To give your arch the support it needs, your foot and ankle surgeon may provide you with an ankle brace or a custom orthotic device that fits into the shoe. Immobilization. Sometimes a short-leg cast or boot is worn to immobilize the foot and allow the tendon to heal, or you may need to completely avoid all weight-bearing for a while. Physical therapy. Ultrasound therapy and exercises may help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle following immobilization. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Shoe modifications. Your foot and ankle surgeon may advise changes to make with your shoes and may provide special inserts designed to improve arch support.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually performed when non-surgical measures have failed. The goal of surgery is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve a patient?s mobility. More than one technique may be used, and surgery tends to include one or more of the following. The tendon is reconstructed or replaced using another tendon in the foot or ankle The name of the technique depends on the tendon used. Flexor digitorum longus (FDL) transfer. Flexor hallucis longus (FHL) transfer. Tibialis anterior transfer (Cobb procedure). Calcaneal osteotomy - the heel bone may be shifted to bring your heel back under your leg and the position fixed with a screw. Lengthening of the Achilles tendon if it is particularly tight. Repair one of the ligaments under your foot. If you smoke, your surgeon may refuse to operate unless you can refrain from smoking before and during the healing phase of your procedure. Research has proven that smoking delays bone healing significantly.